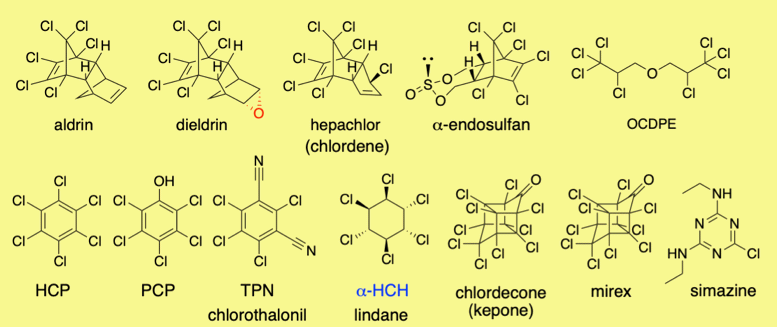
Biodegradation of organochlorine pesticides "DRINS" 2016.8

Organochlorine insecticides, including dieldrin, are synthetic chemicals, some of which have been extensively used for controlling diseases of humans and domestic animals carried by insects and mites. They have also been used against insect pests that greatly damage agricultural crops. Due to their efficiency as insecticides, these compounds were originally considered to be a boon to agriculture and medical entomology. However, their use has been prohibited in many countries since the 1970s because of their biological magnification, high toxicity, and long persistence in the environment. Organochlorine insecticides are still found in the environment more than 30 years after their prohibition.
We have studied biodegradation of dieldrin for bioremediation of the polluted soils.
1. Aerobic dieldrin-degrading fungus, Mucor racemosus strain DDF, was isolated from the soil, to which endosulfan had been annually applied for a long period. Strain DDF was able to degrade dieldrin more than 90% for 10 days incubation at 25°C. Approximately 9.1% of aldrin trans-diol was generated for 1 day incubation when dieldrin degraded.
2. Aerobic dieldrin-degrading fungus, Pseudonocardia sp. strain KSF27, isolated by an enrichment culture in a soil-charcoal perfusion system, converted dieldrin to dihydrochloridenedicarboxylic acid.
While in Mucor racemosus DDF, phosphorylation occorred to give aldrin trans-diol 6-exo-phosphate. This is the 1st case for microorganisms. The metabolites were identified by synthetic studies using microwave-asssisted sulfation etc.
3. A White rot fungus, Phlebia sp. conveted dieldrin to 9-syn-hydroxydieldrin.
4. An aerobic bacterium, Rhodococcus koreensis S1-1, isolated from endosulfan-applied soil, degrades endosulfan sulfate to endosulfan diol monosulfate. Microwave irradiated sulfation reaction was used for the synthesis of plaubible compounds.
5. Degradation of octachlorodipropyl ether (OCDPE) is investigated.(Dr Kazuhiro Takagi (National Institute for Agro-Environmental Scienses), Prof. R. Kondo (Kyushu Univ.), Prof. I. Kamei (Miyazaki Univ.), Prof. Cao, Hai-Qun (Anhui Agric. Univ., China), Yuta Nagashima, Yuuki Sato)
238. "Biochemical Characterisation of NADH:FMN Oxidoreductase HcbA3 from Nocardioides sp. PD653 in Catalysing Aerobic HCB Dechlorination"
Koji Ito, Kazuhiro Takagi, Ryota Kataoka, Hiromasa Kiyota, J. Pestic. Sci. 45(3), 125-131 (2020). 10.1584/jpestics.D20-23235. "Dehalogenation and Dissipation of Chloroaromatic Compounds by Nocardioides sp. PD653: Characterization of the Substrate Specificity"
Koji Ito, Kazuhiro Takagi, Ryota Kataoka, Hiromasa Kiyota, Akio Iwasaki, J. Pestic. Sci. 44(3), 171-176 (2019).209. "Isolation of Endosulfan Sulfate-degrading Rhodococcus koreensis strain S1-1 from Endosulfan Contaminated Soil and Identification of a Novel Metabolite, Endosulfan Diol Monosulfate"
Koji Ito, Fujimasa Kawashima, Ryota Kataoka, Masaaki Kotake, Hiromasa Kiyota, Kenichi Yamazaki, Futa Sakakibara, Sanae Okada, Kazuhiro Takagi, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 473 (4), 1094-1099 (2016).205. "Hydrolysis of Octachlorodipropyl Ether Photolysis in Aqueous Solution"
Yan-Hong Shi, Min Liao, Hiromasa Kiyota, Ri-Mao Hua, Xiang-Wei Wu, Jun Tang, Hai-Qun Cao, Furesen. Environ. Bull., 24, 2534-2539 (2015).203. "Kinetics of Octachlorodipropyl Ether Photolysis in Aqueous Solution"
Yan-Hong Shi, Min Liao, Hiromasa Kiyota, Hai-Qun Cao, Ri-Mao Hua, Feng Tang, Yong-De Yue, J. Pesticide Sci., 40, 49-54 (2015).196. "Novel Phosphorylation of Aldrin-trans-diol by Dieldrin-degrading Fungus Mucor racemosus strain DDF"
Ken-ichi Yamazaki, Kazuhiro Takagi, Ryota Kataoka, Masaaki Kotake, Teiko Yamada, Hiromasa Kiyota, Int. Biodet. Biodeg., 92, 36-40 (2014).166. "Novel metabolic pathways of organochlorine pesticides dieldrin and aldrin by the white rot fungi of the genus Phlebia"
Pengfei Xiao, Toshio Mori, Ichiro Kamei, Hiromasa Kiyota, Kazuhiro Takagi, Ryuichiro Kondo, Chemosphere, WEB (2011).159. "Isolation and identification of dieldrin-degrading Pseudonocardia sp. strain KSF27 using a soil-charcoal perfusion method with aldrin trans-diol as a structural analog of dieldrin"
Futa Sakakibara, Kazuhiro Takagi, Ryota Kataoka, Hiromasa Kiyota, Yuki Sato, Sanae Okada, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 411, 76-81 (2011).146. "Biodegradation of Dieldrin by a Soil Fungus Isolated from a Soil with Annual Endosulfan Application"
Ryota Kataoka, K. Takagi, Ichiro Kamei, Hiromasa Kiyota, Yuuki Sato, Environ Sci. Technol., 44, 6343-6349 (2010).
Effects of Highly Volatile Organochlorine Solvents on Soil Ecosystem
(at the Univ of Tokyo)
The effects of highly volatile organochlorine solvents (1,1,1-trichloroethane, TCET; trichloroethylene, TCE; and tetrachloroethylene, PCE) on soil respiration and soil biomass were investigated using volcanic ash soil and gray lowland soil with different fertilizations. All the solvents significantly inhibited the activity and decreased the biomass under the sealed conditions 10 to 50 mg/gds solvents added. Under the upland and flooded conditions no significant difference between the solvents was observed. Taking into account the solubility of the solvents (TCET > TCE >> PCE) in water, the toxicity would be an order of PCE > TCE > TCET. Buffer ability, resulted from absorption of solvents on organic matters etc., was higher when the soil with organic manure fertilized was used. In addition, the effects were smaller on volcanic ash soil.
97. "Effects of Highly Volatile Organochlorine Solvents on Soil Respiration and Microbial Biomass"
H. Kiyota, S. Kanazawa, A. Yokoyama, H. Wada, Int. J. Soil Sci., 1, 235-242 (2006).
176. "Effects of Highly Volatile Organochlorine Solvents on Soil Nitrogen Cycle and Microbial Counts"
H. Kiyota, S. Ohtsuka, A. Yokoyama, S. Matsumoto, H. Wada, S. Kanazawa, Soil Wat. Res., 7, 109-116 (2012).
Effects of Fluorine-Containing Pesticides on Soil Ecosystem
Effects of fluorine-containing organic compounds such as flutranil and trifluorotoluene on soil microbial activity were investigatied.
A new method to estimate L-glutaminase and L-asparaginase in soils
The indophenol method was applied to the assay of NH4+ for soil L-glutaminase and L-asparaginase activities.30. "Estimation of L-Glutaminase and L-Asparaginase Activities in Soils by the Indophenol Method"
9."Effect of Fertilizer and Manure Application on L-Glutaminase and L-Asparaginase Activities in Soils"
S. Kanazawa and H. Kiyota, Soil Science and Plant Nutrition,41(2), 305-311 (1995).
S. Kanazawa and H. Kiyota, Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 46(3), 741-744 (2000).